

- HGH Deficiency
- So you took a look at yourself in a mirror recently and your heart sank by what you saw.
- Can Human Growth Hormones Really Reverse the Signs of Aging
- We hear about HGH or human growth hormone supplements far more often than we did just a few years ago.
- HGH Benefits for Men
- There are several benefits that males can derive from HGH use, although these are mostly off-label.
- How to Handle an HGH Deficiency in Adults?
- our physician tells you that you have a human growth hormone deficiency or HGH deficiency – now what? What does this mean?
- HGH Use for Bodybuilding
- Human growth hormone (HGH) is considered highly essential for the health and wellbeing of an average person.
- GenF20Plus Double Blind Clinical Study Shows Results That are Promising
- The market is full of unproven HGH products, but only the manufacturer of Genf20 Plus has taken the time to conduct a double blind clinical study.
Latest Findings in Anti-Aging Research
The search for the elusive "fountain of youth" has been on for centuries. Some breakthroughs have been recorded in the quest to combat aging, but nothing has yet delivered the magical effect to satisfy all. So the search has to continue. We present findings from some of the latest anti-aging research that has been released as of 2017.
Researchers identify anti-aging male hormone
Some Brazilian and American researchers have been able to identify a
synthetic male hormone which may help to slow the impact of aging during
a clinical trial. This revelation further confirms the long-held belief
that the human body has the ability to repair itself.
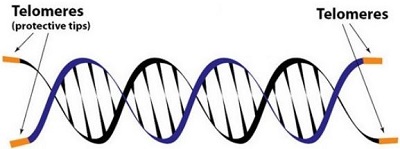
The male hormone known as danazol was used by the researchers to ramp up the levels of telomerase, a prominent enzyme that has been associated to the aging process, in the body. The finding confirmed earlier studies that showed cell aging can be halted or slowed by increasing telomerase.
The enzyme provides protection to short segments of DNA known as telomeres and found at the end of chromosomes. The telomeres shorten every time a cell divides and, if nothing is done to check this, they become so short that the cell loses its function or dies off. Telomerase not only prevent this from happening, but may also assist in the cell division process. A little over 100 telomere base pairs are lost every two years under normal conditions. But as many as 600 telomere base pairs may be lost over similar period when there is serious telomerase deficiency. This is why the danazol study is especially interesting.
The synthetic male hormone was administered to 27 patients suffering from aplastic anemia – a condition brought about by telomerase gene mutation and capable of accelerating aging. Treatment was done with danazol for about two years. The researchers observed that the hormone halted telomere shortening and patients had an average increase of 386 telomere base pairs. The treatment also enhanced hemoglobin mass, eliminating need for blood transfusions.
Telomerase can not only help fight aging, but can also assist in fighting awful diseases and conditions such as cancer. The finding does not necessarily mean danazol will dramatically enhance longevity, but that it can help people age gracefully. It should be noted as well that sex hormones do come with side effects.
Easter Island native compound continues to show promise for anti-aging
Scientists have continued to be thrilled by the potential of the substance rapamycin in reversing aging. This naturally-occurring compound is found in the vicinity of the statues of Easter Island.
The compound was discovered in a soil sample collected by a team of researchers in 1964, according to an article in Chemical and Engineering News. It was eventually observed that rapamycin could help in slowing the aging process. It fights fungus, prevents cells from dividing and serves as an immunosuppressant.
Rapamycin, a by-product of a type of soil bacterium, has been shown in a series of studies on mice and other animals to promote longevity. It has been used to expand the lifespan of worms, yeast and fruit flies by around 25 percent. The ability of the substance to do this has been traced to its effectiveness in regulating the expression of a type of protein known as mTOR.
This compound is considered the most effective of all drugs recently evaluated by federally-funded laboratories for combating aging and its associated diseases. A 2014 Novartis study suggested rapamycin enhances the immune systems of older patients.
In a mice study, scientists observed males and females that received the compound lived around 9 and 14 longer respectively, in comparison to those in the placebo group.
However, it is feared that rapamycin use for anti-aging may be accompanied by unknown, long-term side effects.
Researchers find potent anti-aging compound in pomegranates
Analysis of pomegranates by a team of Swiss scientists has revealed
anti-aging potential of a compound produced from the fruit. In
preliminary findings published in Nature Medicine, the researchers from
Switzerland's Federal Institute of Technology in Lausanne posited that
consumption of pomegranates leads to production of the molecule
urolithin A (UA for short), which is what actually delivers its
anti-aging benefits.

Pomegranates do not contain urolithin A in themselves. Instead, the juice of this tropical fruit contains natural substances called ellagitannins. These substances are broken down and converted into urolithin A in the stomach through the help of intestinal bacteria.
The researchers, who worked in collaboration with the biotechnology company Amazentis, noted that urolithin A is beneficial in slowing aging as a result of its ability to boost muscle cell protection. The substance helps to restore ability of cells to repair and revive defective mitochondria, which are the main power houses of cells. Failing mitochondria is responsible for the onset of a variety of age-related diseases, including Parkinson's disease.
Study co-author Patrick Aebischer described the molecule as the only one known to be capable of reviving mitochondrial cleanup (mitophagy).
Old nematode worms treated with urolithin A derived from pomegranates lived 45 percent longer than those in the placebo group. Elderly mice that got the same substance also showed 42 percent improvement in endurance running, compared to those in the control group.
It is not entirely clear yet if urolithin A produced from pomegranate consumption would deliver similar benefits in humans. However, it appears this approach may work, but the extent of effectiveness is not yet known.
It is also worth stating that the amount of urolithin A produced in the stomach varies between individuals. Some persons are also thought unable to produce this compound, regardless of how many pomegranates are consumed.
Amazentis is reportedly conducting human clinical trials in Europe with the aim of producing perfect doses of UA for those who might be interested in tapping into its benefits.
International researchers looking to test anti-aging drug in humans
An international group of researchers from St. Louis' Washington University and Japan's Kelo University think they may have found a compound that could ultimately become the elusive fountain of youth. This belief is based on evidence from mice studies.
The researchers have been evaluating the anti-aging benefits of the compound nicotinamide mono nucleotide (NMN) and seemed impressed by what they have seen. Studies have shown that this substance promotes longevity in mice. The results obtained by the researchers have been so impressive that NMN has been billed the first anti-aging that will be tested on humans.
Nicotinamide mono nucleotide is believed to activate a type of proteins called sirtuins, which naturally drops as people grow older. It has also been shown that the compound helps deal with declines in vision quality and metabolism. NMN has been proven beneficial for dealing with glucose intolerance in mice and in reversing diabetes.
The human tests planned for August will see the researchers administer NMN to 10 people to determine if it does offer any anti-aging benefits to humans. It will become the first anti-aging drug available to the public if found safe and approved for human use.
Metformin, nicotinamide riboside show good anti-aging potential
A number of drugs have been shown in clinical trials to prolong the lifespan of animals. However, the effectiveness of these drugs in promoting longevity in humans is mostly unconfirmed. But metformin and nicotinamide riboside are two of the drugs that have shown good promise in combating aging in humans.
Metformin is a drug commonly used for treating Type II diabetes. Anti-aging is an off-label benefit of this drug that has been observed by researchers. It has been shown to make mice live up to 40 percent longer. In a study at Cardiff University, the use of metformin was observed to cause diabetics using it to live an average of eight years longer than their non-diabetic counterparts. It promotes longevity by making more oxygen available to cells in the body.
A clinical trial tagged Targeting Aging With Metformin (TAME) has been approved by the FDA to ascertain how the diabetes drug can be beneficial for fighting aging. The trial will focus on 3,000 elderly individuals aged between 70 and 80.
Research carried out by a team of scientists headed by Johan Auwerx revealed nicotinamide riboside may promote longevity in humans as well. The compound revitalizes stem cells in mice resulting in improved cell regeneration in muscle tissue. This helps to protect the body against the effect of aging.
Progress is obviously being made in anti-aging research, although the so much talked about "fountain of youth" still remains elusive for now. One thing that appears certain is that the search for the ultimate anti-aging solution will continue. This is especially so given the belief that aging is the biggest factor in the onset of debilitating conditions in older people. Everything possible must be done to moderate or slow it. As for now you may consider HGH therapy as many have already been using it to slow down aging.
Feel Years Younger With Genf20 Plus Or Your Money Back!
REFERENCES
www.worldhealth.net/news/new-hormone-can-regenerate-aging-cells-found-human/
www.aol.com/article/2016/08/01/could-easter-island-hold-the-key-to-anti-aging/21442714/
gizmodo.com/pomegranates-yield-promising-anti-aging-compound-1783513898
https://www.good.is/articles/fountain-of-youth-for-mice
www.natureworldnews.com/articles/24933/20160708/humans-extend-lives-30-years-anti-aging-drugs.htm
mobile.nytimes.com/2016/05/17/us/aging-research-disease-dogs.html?_

- "A lot of great info on HGH therapy and HGH supplements"
- Stan (Fort Lauderdale)
- "I almost started using prescription HGH injections but because of the high cost involved and the long list of side effects I opted for Genf20 plus instead and I was glad I did!"
- Jenifer (Los Angeles)
- "Before buying Genf20 Plus You must read the reviews at genf20plus.info"
- Eric (San Diego)
- "Thanks for showing both the benefits and the risks of using HGH"
- Nancy (NYC)
- Latest Articles
- All You Need to Know About HGH Replacement Therapy
- Human growth hormone (HGH) is required for some essential functions in the body.
- Maximize Your HGH Levels With Genf20 Plus, Diet and Lifestyle Choices
- Taking the HGH supplement can also help your pituitary gland to produce more HGH.
- Does Human Growth Hormone Work for Weight Loss?
- In addition to using HGH supplements you should consider intensive exercise and intermittent fasting.
- Gynecomastia in Men and How HGH Affects It
